102864: [AtCoder]ABC286 E - Souvenir
Description
Score : $500$ points
Problem Statement
There are $N$ cities. There are also one-way direct flights that connect different cities.
The availability of direct flights is represented by $N$ strings $S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_N$ of length $N$ each.
If the $j$-th character of $S_i$ is Y, there is a direct flight from city $i$ to city $j$;
if it is N, there is not.
Each city sells a souvenir; city $i$ sells a souvenir of value $A_i$.
Consider the following problem:
Takahashi is currently at city $S$ and wants to get to city $T$ (that is different from city $S$) using some direct flights.
Every time he visits a city (including $S$ and $T$), he buys a souvenir there.
If there are multiple routes from city $S$ to city $T$, Takahashi decides the route as follows:
- He tries to minimize the number of direct flights in the route from city $S$ to city $T$.
- Then he tries to maximize the total value of the souvenirs he buys.
Determine if he can travel from city $S$ to city $T$ using the direct flights. If he can, find the "number of direct flights" and "total value of souvenirs" in the route that satisfies the conditions above.
You are given $Q$ pairs $(U_i,V_i)$ of distinct cities.
For each $1\leq i\leq Q$, print the answer to the problem above when $S=U_i$ and $T=V_i$.
Constraints
- $2 \leq N \leq 300$
- $1\leq A_i\leq 10^9$
- $S_i$ is a string of length $N$ consisting of
YandN. - The $i$-th character of $S_i$ is
N. - $1\leq Q\leq N(N-1)$
- $1\leq U_i,V_i\leq N$
- $U_i\neq V_i$
- If $i \neq j$, then $(U_i,V_i)\neq (U_j,V_J)$.
- $N,A_i,Q,U_i$, and $V_i$ are all integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
$N$ $A_1$ $A_2$ $\ldots$ $A_N$ $S_1$ $S_2$ $\vdots$ $S_N$ $Q$ $U_1$ $V_1$ $U_2$ $V_2$ $\vdots$ $U_Q$ $V_Q$
Output
Print $Q$ lines.
The $i$-th $(1\leq i\leq Q)$ line should contain
Impossible if he cannot travel from city $U_i$ to city $V_i$;
if he can, the line should contain "the number of direct flights" and "the total value of souvenirs" in the route chosen as described above, in this order, separated by a space.
Sample Input 1
5 30 50 70 20 60 NYYNN NNYNN NNNYY YNNNN YNNNN 3 1 3 3 1 4 5
Sample Output 1
1 100 2 160 3 180
For $(S,T)=(U_1,V_1)=(1,3)$, there is a direct flight from city $1$ to city $3$, so the minimum possible number of direct flights is $1$, which is achieved when he uses that direct flight. In this case, the total value of the souvenirs is $A_1+A_3=30+70=100$.
For $(S,T)=(U_2,V_2)=(3,1)$, the minimum possible number of direct flights is $2$. The following two routes achieve the minimum: cities $3\to 4\to 1$, and cities $3\to 5\to 1$. Since the total value of souvenirs in the two routes are $70+20+30=120$ and $70+60+30=160$, respectively, so he chooses the latter route, and the total value of the souvenirs is $160$.
For $(S,T)=(U_3,V_3)=(4,5)$, the number of direct flights is minimum when he travels cities $4\to 1\to 3\to 5$, where the total value of the souvenirs is $20+30+70+60=180$.
Sample Input 2
2 100 100 NN NN 1 1 2
Sample Output 2
Impossible
There may be no direct flight at all.
Input
题意翻译
#### 题目描述 从前有 $n$ 座岛,每个岛上有 $a_i$ 个金币,各个岛间有若干条单向航线相连。 你从某个岛开始旅行,经过一个岛(包括最开始所在的岛)就会拿走上面的金币。 现在问你 $q$ 个问题:从岛 $u_i$ 旅行到岛 $v_i$,最少要走几条航线,以及恰好走这么多条航线最多能获得多少金币。如果根本无法到达 $v_i$,输出 `Impossible`。 询问之间相互独立。 #### 输入格式 输入第一行一个整数 $n$ 表示岛的数量。 接下来一行 $n$ 个整数表示每个岛上的金币数。 接下来 $n$ 行每行一个长为 $n$ 的字符串,第 $i$ 行字符串的第 $j$ 个字符若为 `Y` 则表示岛 $i$ 和 $j$ 间有单向航线,否则表示没有。 接下来一行一个整数 $q$ 表示询问次数。 最后 $q$ 行每行两个整数 $u_i,v_i$,询问你从岛 $u_i$ 旅行到岛 $v_i$ 最少要走几条航线,以及恰好走这么多条航线最多能获得多少金币。 #### 输出格式 对于每个询问输出一行: - 若 $u_i$ 不能到达 $v_i$,输出 `Impossible`; - 否则,输出从岛 $u_i$ 旅行到岛 $v_i$ 最少要走几条航线,以及恰好走这么多条航线最多能获得多少金币。 #### 样例解释 1 这些岛的结构如下: 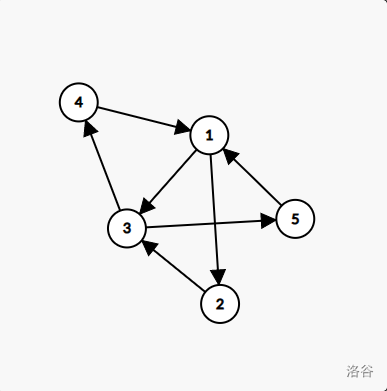 - 对于第 $1$ 个询问,因为岛 $1$ 有一条航线通往岛 $3$,显然最少航线为 $1$ 条,此时能拿到岛 $1$ 和岛 $3$ 上的金币共 $30+70=100$ 个。 - 对于第 $2$ 个询问,可以证明最少航线为 $2$ 条,有两种方案 $3 \rarr 4 \rarr 1$ 和 $3 \rarr 5 \rarr 1$,总金币分别为 $70+20+30=120$ 和 $70+60+30=160$,故最多金币为 $160$。 - 对于第 $3$ 个询问,只有一种方案 $4 \rarr 1 \rarr 3 \rarr 5$ 可以使航线数最少为 $3$,所得金币为 $20+30+70+60=180$。 #### 样例解释 2 笑死,连航线都没有。 #### 数据范围与约定 对于 $100\%$ 的数据,$2\le n\le 300,1\le a_i\le 10^9,1\le q\le n(n-1),1\le u_i,v_i\le n$,且询问中的 $u_i,v_i$ 各不相同。 翻译者:[not_Rick_Astley](https://www.luogu.com.cn/user/689673)Output
得分:$500$分
问题描述
有$N$个城市。还有一条连接不同城市的单程直达航班。
直达航班的可用性由长度为$N$的$N$个字符串$S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_N$表示。
如果$S_i$的第$j$个字符是Y,则从城市$i$到城市$j$有直达航班;
如果是N,则没有。
每个城市都出售一种纪念品;城市$i$出售价值$A_i$的纪念品。
考虑以下问题:
Takahashi目前在城市$S$,希望通过一些直达航班到达城市$T$(与城市$S$不同)。 每次他访问一个城市(包括$S$和$T$),他都会在那里购买纪念品。
如果从城市$S$到城市$T$有多条路线,Takahashi会按照以下方式决定路线:
- 他试图最小化从城市$S$到城市$T$的路线中的直达航班数量。
- 然后他试图最大化他购买的纪念品的总价值。
确定他是否可以使用直达航班从城市$S$到城市$T$旅行。 如果可以,请找到满足上述条件的路线中的“直达航班数量”和“纪念品总价值”。
给你$Q$对不同的城市$(U_i,V_i)$。
对于每$1\leq i\leq Q$,当$S=U_i$和$T=V_i$时,输出上述问题的答案。
约束
- $2 \leq N \leq 300$
- $1\leq A_i\leq 10^9$
- $S_i$是一个由
Y和N组成的长度为$N$的字符串。 - $S_i$的第$i$个字符是
N。 - $1\leq Q\leq N(N-1)$
- $1\leq U_i,V_i\leq N$
- $U_i\neq V_i$
- 如果$i \neq j$,则$(U_i,V_i)\neq (U_j,V_J)$。
- $N,A_i,Q,U_i$和$V_i$都是整数。
输入
输入从Standard Input以以下格式给出:
$N$ $A_1$ $A_2$ $\ldots$ $A_N$ $S_1$ $S_2$ $\vdots$ $S_N$ $Q$ $U_1$ $V_1$ $U_2$ $V_2$ $\vdots$ $U_Q$ $V_Q$
输出
输出$Q$行。
第$i$行($1\leq i\leq Q$)应包含
如果他不能从城市$U_i$到城市$V_i$旅行,则为Impossible;
如果可以,则应包含如上所述的路线中“直达航班数量”和“纪念品总价值”,顺序以空格分隔。
样例输入1
5 30 50 70 20 60 NYYNN NNYNN NNNYY YNNNN YNNNN 3 1 3 3 1 4 5
样例输出1
1 100 2 160 3 180
对于$(S,T)=(U_1,V_1)=(1,3)$,从城市$1$到城市$3$有直达航班, 因此直达航班的最小可能数量为$1$,当使用该直达航班时可以达到。 在这种情况下,纪念品的总价值为$A_1+A_3=30+70=100$。
对于$(S,T)=(U_2,V_2)=(3,1)$,直达航班的最小可能数量为$2$。 以下两条路线可以达到最小值:城市$3\to 4\to 1$和城市$3\to 5\to 1$。 由于两条路线中的纪念品总价值分别为$70+20+30=120$和$70+60+30=160$, 因此他选择后者路线,纪念品的总价值为$160$。
对于$(S,T)=(U_3,V_3)=(4,5)$,当他旅行城市$4\to 1\to 3\to 5$时,直达航班的数量是最小的,纪念品的总价值为$20+30+70+60=180$。
样例输入2
2 100 100 NN NN 1 1 2
样例输出2
Impossible
可能根本没有任何直达航班。