310352: CF1818D. Fish Graph
Description
You are given a simple undirected graph with $n$ nodes and $m$ edges. Note that the graph is not necessarily connected. The nodes are labeled from $1$ to $n$.
We define a graph to be a Fish Graph if it contains a simple cycle with a special node $u$ belonging to the cycle. Apart from the edges in the cycle, the graph should have exactly $2$ extra edges. Both edges should connect to node $u$, but they should not be connected to any other node of the cycle.
Determine if the graph contains a subgraph that is a Fish Graph, and if so, find any such subgraph.
In this problem, we define a subgraph as a graph obtained by taking any subset of the edges of the original graph.
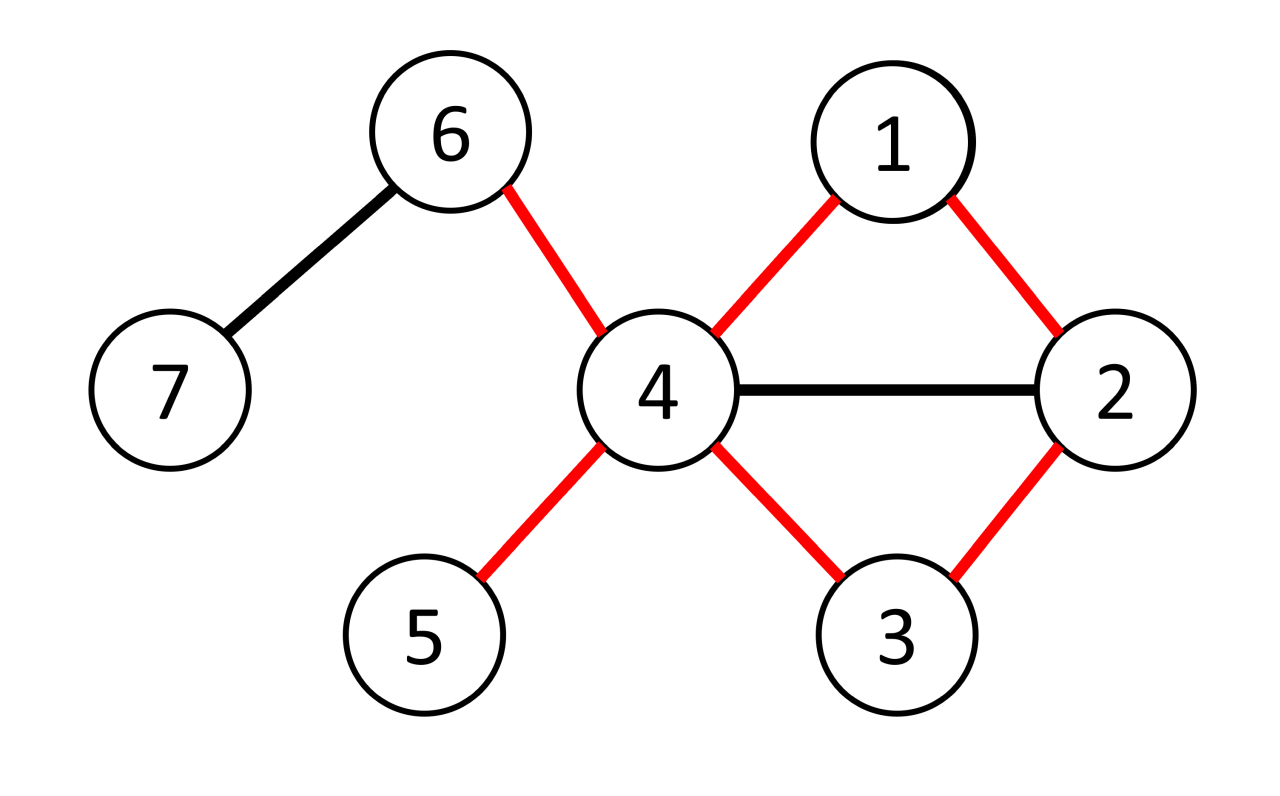 Visualization of example 1. The red edges form one possible subgraph that is a Fish Graph.
Visualization of example 1. The red edges form one possible subgraph that is a Fish Graph. The first line of input contains the integer $t$ ($1 \leq t \leq 1000$), the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers, $n$ and $m$ ($1 \le n, m \le 2\,000$) — the number of nodes and the number of edges.
Each of the next $m$ lines contains the description of an edge. Each line contains two integers $u_i$ and $v_i$ ($1 \leq u_i, v_i \leq n$, $u_i\neq v_i$) — an edge connects node $u_i$ to node $v_i$.
It is guaranteed that no two edges connect the same unordered pair of nodes.
Furthermore, it is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ and the sum of $m$ over all test cases both do not exceed $2\,000$.
OutputFor each testcase, output "YES" if the graph contains a subgraph that is a Fish Graph, otherwise print "NO". If the answer is "YES", on the following lines output a description of the subgraph.
The first line of the description contains one integer $k$ — the number of edges of the subgraph.
On the next $k$ lines, output the edges of the chosen subgraph. Each of the $k$ lines should contains two integers $u$ and $v$ ($1\le u, v\le n$, $u\neq v$) — the edge between $u$ and $v$ belongs to the subgraph. The order in which $u$ and $v$ are printed does not matter, as long as the two nodes are connected by an edge in the original graph. The order in which you print the edges does not matter, as long as the resulting subgraph is a fish graph.
If there are multiple solutions, print any.
ExampleInput3 7 8 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 4 5 4 6 4 2 6 7 7 7 6 7 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 1 3 3 5 4 4 1 3 3 4 4 1 1 2Output
YES 6 5 4 6 4 4 3 1 4 2 1 3 2 YES 5 5 3 2 3 3 1 4 3 1 4 NONote
In the first example, a possible valid subgraph contains the cycle $1 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 1$. The special node of this cycle is node $4$. The two extra edges $4 - 5$ and $4 - 6$ are both connected to $4$, completing the Fish Graph.
In the second example, a possible valid subgraph contains the cycle $1 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 1$. The special node of this cycle is node $3$. The two extra edges $3 - 2$ and $3 - 5$ are both connected to $3$, completing the Fish Graph.
In the last example, it can be proven that there is no valid subgraph.
Input
Output
输入数据格式:第一行包含一个整数t(1≤t≤1000),表示测试用例的数量。接下来是t个测试用例的描述。每个测试用例的第一行包含两个整数n和m(1≤n, m≤2000),分别表示节点数和边数。接下来的m行,每行包含两个整数ui和vi(1≤ui, vi≤n,ui≠vi),表示节点ui和节点vi之间的一条边。
输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,如果图中包含一个“鱼形图”子图,则输出"YES",否则输出"NO"。如果答案为"YES",则在接下来的几行中输出子图的描述。描述的第一行包含一个整数k,表示子图的边数。接下来的k行,每行输出子图的一条边,格式为两个整数u和v(1≤u, v≤n,u≠v),表示节点u和节点v之间的边。如果有多个解决方案,输出任意一个。
公式用latex格式表示:
- 输入数据格式:\[t, (n, m), (u_1, v_1), (u_2, v_2), ..., (u_m, v_m)\]
- 输出数据格式:\[ \text{"YES"} \] 或 \[ \text{"NO"} \]
- 如果是"YES",则跟随k和k条边:\[k, (u_1, v_1), (u_2, v_2), ..., (u_k, v_k)\]题目大意:判断给定的简单无向图中是否包含一个“鱼形图”子图。一个“鱼形图”定义为包含一个简单环和特殊节点u的图。除了环中的边,图应该恰好有2条额外的边,这两条边都应该连接到节点u,但不应连接到环中的任何其他节点。 输入数据格式:第一行包含一个整数t(1≤t≤1000),表示测试用例的数量。接下来是t个测试用例的描述。每个测试用例的第一行包含两个整数n和m(1≤n, m≤2000),分别表示节点数和边数。接下来的m行,每行包含两个整数ui和vi(1≤ui, vi≤n,ui≠vi),表示节点ui和节点vi之间的一条边。 输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,如果图中包含一个“鱼形图”子图,则输出"YES",否则输出"NO"。如果答案为"YES",则在接下来的几行中输出子图的描述。描述的第一行包含一个整数k,表示子图的边数。接下来的k行,每行输出子图的一条边,格式为两个整数u和v(1≤u, v≤n,u≠v),表示节点u和节点v之间的边。如果有多个解决方案,输出任意一个。 公式用latex格式表示: - 输入数据格式:\[t, (n, m), (u_1, v_1), (u_2, v_2), ..., (u_m, v_m)\] - 输出数据格式:\[ \text{"YES"} \] 或 \[ \text{"NO"} \] - 如果是"YES",则跟随k和k条边:\[k, (u_1, v_1), (u_2, v_2), ..., (u_k, v_k)\]