310494: CF1842E. Tenzing and Triangle
Description
There are $n$ pairwise-distinct points and a line $x+y=k$ on a two-dimensional plane. The $i$-th point is at $(x_i,y_i)$. All points have non-negative coordinates and are strictly below the line. Alternatively, $0 \leq x_i,y_i, x_i+y_i < k$.
Tenzing wants to erase all the points. He can perform the following two operations:
- Draw triangle: Tenzing will choose two non-negative integers $a$, $b$ that satisfy $a+b<k$, then all points inside the triangle formed by lines $x=a$, $y=b$ and $x+y=k$ will be erased. It can be shown that this triangle is an isosceles right triangle. Let the side lengths of the triangle be $l$, $l$ and $\sqrt 2 l$ respectively. Then, the cost of this operation is $l \cdot A$.
The blue area of the following picture describes the triangle with $a=1,b=1$ with cost $=1\cdot A$.
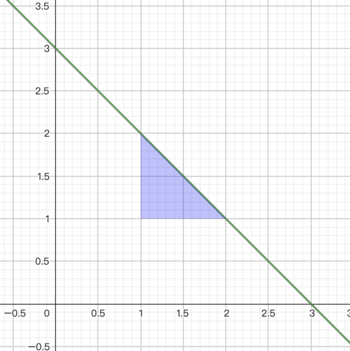
- Erase a specific point: Tenzing will choose an integer $i$ that satisfies $1 \leq i \leq n$ and erase the point $i$. The cost of this operation is $c_i$.
Help Tenzing find the minimum cost to erase all of the points.
InputThe first line of the input contains three integers $n$, $k$ and $A$ ($1\leq n,k\leq 2\cdot 10^5$, $1\leq A\leq 10^4$) — the number of points, the coefficient describing the hypotenuse of the triangle and the coefficient describing the cost of drawing a triangle.
The following $n$ lines of the input the $i$-th line contains three integers $x_i,y_i,c_i$ ($0\leq x_i,y_i,x_i+y_i< k$, $1\leq c_i\leq 10^4$) — the coordinate of the $i$-th points and the cost of erasing it using the second operation. It is guaranteed that the coordinates are pairwise distinct.
OutputOutput a single integer —the minimum cost needed to erase all of the points.
ExamplesInput4 6 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 6Output
4Input
6 7 1 4 2 1 3 3 1 5 1 4 3 2 5 4 1 1 0 6 4Output
4Input
10 4 100 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 50 0 3 200 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 0 200 2 1 200 3 0 200Output
355Note
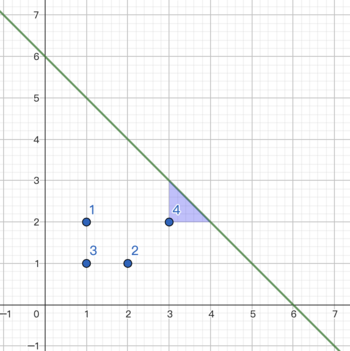
The picture of the first example:
Tenzing do the following operations:
- draw a triangle with $a=3,b=2$, the cost $=1\cdot A=1$.
- erase the first point, the cost $=1$.
- erase the second point, the cost $=1$.
- erase the third point, the cost $=1$.
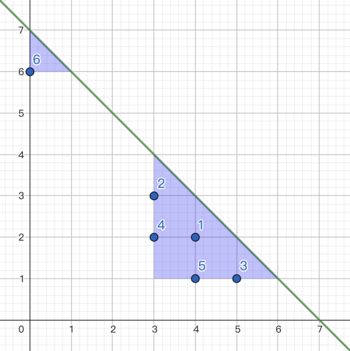
The picture of the second example:
Input
题意翻译
给定 $n$ 个形如 $(x,y,c)$ 的数对,表示在平面直角坐标系中,$(x,y)$ 上有一个权值为 $c$ 的点。 现在,丁真同学想要删掉这 $n$ 个点。 两种删点方法: 1. 选择一个点 $i$ 删去,代价为 $c_i$。 2. 任选一个点 $(x_0,y_0)$,这个点要满足 $x_0+y_0<k,x_0,y_0 \ge 0$,删除所有满足 $x_i \ge x_0, y_i \ge y_0$ 的点,代价为 $l \times A$,其中 $l$ 为 $(x_0,y_0)$ 与 $l:x+y=k$ 围成的等腰直角三角形的直角边长。 给定正整数 $k,A$,求最小代价。Output
在一个二维平面上,有n个不同的点,以及一条直线x+y=k。每个点的坐标为(x_i,y_i),所有点的坐标都是非负的,并且严格位于直线x+y=k之下。换句话说,0 <= x_i, y_i, x_i+y_i < k。Tenzing想要擦除所有点,他可以进行以下两种操作:
1. 画三角形:Tenzing选择两个非负整数a和b,满足a+b
2. 擦除一个特定点:Tenzing选择一个整数i,满足1 <= i <= n,并擦除第i个点。这个操作的成本是c_i。
帮助Tenzing找到擦除所有点的最小成本。
输入数据格式:
第一行包含三个整数n, k和A(1≤n,k≤2*10^5, 1≤A≤10^4)——点的数量、描述三角形斜边的系数和描述画三角形成本的系数。
接下来n行,每行包含三个整数x_i, y_i, c_i(0≤x_i,y_i,x_i+y_i
输出数据格式:
输出一个整数——擦除所有点所需的最小成本。题目大意: 在一个二维平面上,有n个不同的点,以及一条直线x+y=k。每个点的坐标为(x_i,y_i),所有点的坐标都是非负的,并且严格位于直线x+y=k之下。换句话说,0 <= x_i, y_i, x_i+y_i < k。Tenzing想要擦除所有点,他可以进行以下两种操作: 1. 画三角形:Tenzing选择两个非负整数a和b,满足a+b