310741: CF1878G. wxhtzdy ORO Tree
Description
After (finally) qualifying for the IOI 2023, wxhtzdy was very happy, so he decided to do what most competitive programmers do: trying to guess the problems that will be on IOI. During this process, he accidentally made a problem, which he thought was really cool.
You are given a tree (a connected acyclic graph) with $n$ vertices and $n-1$ edges. Vertex $i$ ($1 \le i \le n$) has a value $a_i$.
Lets' define $g(u, v)$ as the bitwise or of the values of all vertices on the shortest path from $u$ to $v$. For example, let's say that we want to calculate $g(3, 4)$, on the tree from the first test case in the example. On the path from $3$ to $4$ are vertices $3$, $1$, $4$. Then, $g(3, 4) = a_3 \ | \ a_1 \ | \ a_4$ (here, $|$ represents the bitwise OR operation).
Also, you are given $q$ queries, and each query looks like this:
You are given $x$ and $y$. Let's consider all vertices $z$ such that $z$ is on the shortest path from $x$ to $y$ (inclusive).
Lets define the niceness of a vertex $z$ as the sum of the number of non-zero bits in $g(x, z)$ and the number of non-zero bits in $g(y, z)$. You need to find the maximum niceness among all vertices $z$ on the shortest path from $x$ to $y$.
Since his brain is really tired after solving an output only problem on SIO (he had to do it to qualify for the IOI), he wants your help with this problem.
InputThe first line of input contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of vertices.
The second line of each test case contains $n$ positive integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_v \le 10^9$) — the value of each vertex, the $i$-th integer in this line corresponds to the vertex $i$.
Following $n - 1$ lines are the description of a tree.
Each line contains two integers $u$ and $v$ ($1 \le u, v \le n, u \ne v$) — indicating that vertices $u$ and $v$ are connected by an edge.
The next line contains a single integer $q$ ($1 \le q \le 10^5$) — number of queries.
Following $q$ lines contain 2 integers $x, y$ ($1 \le x, y \le n$) — the vertices $x$ and $y$ for each query.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over all test cases does not exceed $2 \cdot 10^5$.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $q$ over all test cases does not exceed $10^5$.
OutputFor each test case output $q$ integers, each of which is the answer to the corresponding query.
ExamplesInput3 4 1 2 3 4 1 3 1 2 1 4 3 1 1 1 3 1 4 3 7 6 3 3 1 2 1 4 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 3 1 4 1 1 1Output
2 4 3 6 6 6 6 2Input
3 7 4 7 7 4 10 8 10 6 1 3 1 2 1 7 4 1 5 4 2 4 7 5 2 3 4 5 2 5 6 9 5 6 2 4 6 5 1 2 1 1 6 4 3 1 3 4 6 1 1 4 4 3 3 5 7 5 1 3 7 5 1 6 2 1 5 4 2 3 3 4 7 6 6 3 2 4 2 7 7Output
8 6 7 7 6 6 4 7 6 4Input
1 7 6 8 7 2 5 8 7 2 1 3 2 4 3 4 6 4 5 6 7 4 1 5 6 7 4 5 1 4Output
7 7 5 7Note
The image below shows the tree from the second example, first test case.
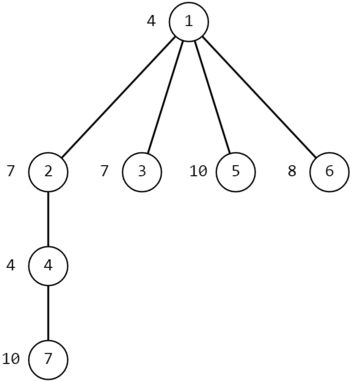 Tree from the second example, first test case
Tree from the second example, first test case In the first query, we have $x=7$, $y=5$. The shortest path from $7$ to $5$ is $7-4-2-1-5$.
Let's calculate the niceness of vertex $7$ on this path. We have $g(7,7)=a_7=10=(1010)_2$ and $g(5,7)=a_5 \ | \ a_1 \ | \ a_2 \ | \ a_4 \ | \ a_7=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 10=15=(1111)_2$, so its niceness is equal to $2 + 4 = 6$.
Now let's calculate the niceness of vertex $4$ on this path. We have $g(7,4)=a_7 \ | \ a_4=10 \ | \ 4=14=(1110)_2$ and $g(5,4)=a_5 \ | \ a_1 \ | \ a_2 \ | \ a_4=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7 \ | \ 4=15=(1111)_2$, so its niceness is equal to $3 + 4 = 7$.
Now let's calculate the niceness of vertex $2$ on this path. We have $g(7,2)=a_7 \ | \ a_4 \ | \ a_2=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7=15=(1111)_2$ and $g(5,2)=a_5 \ | \ a_1 \ | \ a_2=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7=15=(1111)_2$, so its niceness is equal to $4 + 4 = 8$.
Now let's calculate the niceness of vertex $1$ on this path. We have $g(7,1)=a_7 \ | \ a_4 \ | \ a_2 \ | \ a_1=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7 \ | \ 4=15=(1111)_2$ and $g(5,1)=a_5 \ | \ a_1=10 \ | \ 4=14=(1110)_2$, so its niceness is equal to $4 + 3 = 7$.
Finally, let's calculate the niceness of vertex $5$ on this path. We have $g(7,5)=a_7 \ | \ a_4 \ | \ a_2 \ | \ a_1 \ | \ a_5=10 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 7 \ | \ 4 \ | \ 10=15=(1111)_2$ and $g(5,5)=a_5=10=(1010)_2$, so its niceness is equal to $4 + 2 = 6$.
The maximum niceness on this path is at vertex $2$, and it is $8$.
Output
给定一个包含n个顶点和n-1条边的树(无环连通图),每个顶点都有一个值a[i]。定义函数g(u, v)为从u到v最短路径上所有顶点值的按位或(bitwise OR)。对于每个查询,给定x和y,考虑所有在x到y最短路径上的顶点z,定义z的“niceness”为g(x, z)和g(y, z)中非零位的数量之和。你需要找出x到y最短路径上所有顶点的最大“niceness”。
输入输出数据格式:
输入:
- 第一行包含一个整数t(1 ≤ t ≤ 10^4),表示测试用例的数量。
- 每个测试用例的第一行包含一个整数n(1 ≤ n ≤ 2 × 10^5),表示顶点的数量。
- 每个测试用例的第二行包含n个正整数a[1], a[2], ..., a[n](1 ≤ a[v] ≤ 10^9),表示每个顶点的值。
- 接下来的n-1行描述了一棵树,每行包含两个整数u和v(1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v),表示顶点u和v之间有一条边。
- 下一行包含一个整数q(1 ≤ q ≤ 10^5),表示查询的数量。
- 接下来的q行,每行包含2个整数x, y(1 ≤ x, y ≤ n),表示每个查询的顶点x和y。
输出:
- 对于每个测试用例,输出q个整数,每个数是对应查询的答案。题目大意: 给定一个包含n个顶点和n-1条边的树(无环连通图),每个顶点都有一个值a[i]。定义函数g(u, v)为从u到v最短路径上所有顶点值的按位或(bitwise OR)。对于每个查询,给定x和y,考虑所有在x到y最短路径上的顶点z,定义z的“niceness”为g(x, z)和g(y, z)中非零位的数量之和。你需要找出x到y最短路径上所有顶点的最大“niceness”。 输入输出数据格式: 输入: - 第一行包含一个整数t(1 ≤ t ≤ 10^4),表示测试用例的数量。 - 每个测试用例的第一行包含一个整数n(1 ≤ n ≤ 2 × 10^5),表示顶点的数量。 - 每个测试用例的第二行包含n个正整数a[1], a[2], ..., a[n](1 ≤ a[v] ≤ 10^9),表示每个顶点的值。 - 接下来的n-1行描述了一棵树,每行包含两个整数u和v(1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v),表示顶点u和v之间有一条边。 - 下一行包含一个整数q(1 ≤ q ≤ 10^5),表示查询的数量。 - 接下来的q行,每行包含2个整数x, y(1 ≤ x, y ≤ n),表示每个查询的顶点x和y。 输出: - 对于每个测试用例,输出q个整数,每个数是对应查询的答案。