311305: CF1968E. Cells Arrangement
Description
You are given an integer $n$. You choose $n$ cells $(x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2),\dots,(x_n,y_n)$ in the grid $n\times n$ where $1\le x_i\le n$ and $1\le y_i\le n$.
Let $\mathcal{H}$ be the set of distinct Manhattan distances between any pair of cells. Your task is to maximize the size of $\mathcal{H}$. Examples of sets and their construction are given in the notes.
If there exists more than one solution, you are allowed to output any.
Manhattan distance between cells $(x_1,y_1)$ and $(x_2,y_2)$ equals $|x_1-x_2|+|y_1-y_2|$.
InputThe first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1\le t\le 50$) — the number of test cases.
Each of the following $t$ lines contains a single integer $n$ ($2\le n\le 10^3$).
OutputFor each test case, output $n$ points which maximize the size of $\mathcal{H}$. It is not necessary to output an empty line at the end of the answer for each test case.
ExampleInput5 2 3 4 5 6Output
1 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 3 4 3 4 4 1 1 1 3 1 4 2 1 5 5 1 4 1 5 1 6 5 2 5 5 6 1Note
In the first testcase we have $n=2$. One of the possible arrangements is:
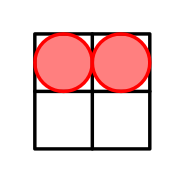 The arrangement with cells located in $(1,1)$ and $(1,2)$.
The arrangement with cells located in $(1,1)$ and $(1,2)$. In the second testcase we have $n=3$. The optimal arrangement is:
 The arrangement with cells located in $(2,1)$, $(2,3)$ and $(3,1)$.
The arrangement with cells located in $(2,1)$, $(2,3)$ and $(3,1)$. $\mathcal{H}$=$\{|2-2|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|3-3|,|3-3|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|1-3|,|2-3|+|1-1|,|2-3|+|3-1|\}$=$\{0,0,0,2,1,3\}$=$\{0,1,2,3\}$.
For $n=4$ a possible arrangement is:
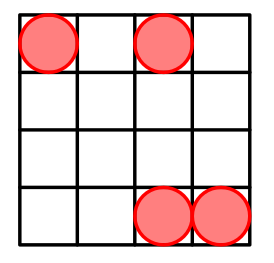
For $n=5$ a possible arrangement is:

For $n=6$ a possible arrangement is:
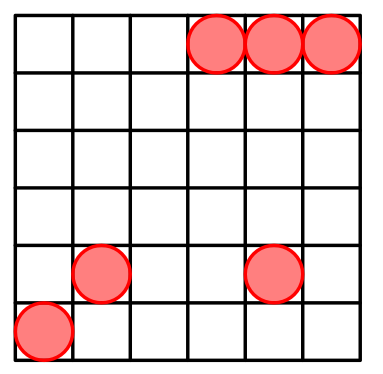
Output
曼哈顿距离:单元格 (x_1,y_1) 和 (x_2,y_2) 之间的曼哈顿距离等于 \(|x_1-x_2|+|y_1-y_2|\)。
输入数据格式:第一行包含一个整数 \(t\)(\(1≤t≤50\))——测试用例的数量。接下来的 \(t\) 行,每行包含一个整数 \(n\)(\(2≤n≤10^3\))。
输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,输出 \(n\) 个点,使得集合 \(\mathcal{H}\) 的大小最大化。每个测试用例的答案结束时不需要输出空行。
示例输入输出已给出,请参考题目描述中的样例。题目大意:给定一个整数n,在n×n的网格中选择n个单元格,单元格的坐标为 (x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2),…,(x_n,y_n),其中 1≤x_i≤n 和 1≤y_i≤n。定义集合 \(\mathcal{H}\) 为任意两个单元格之间的曼哈顿距离的集合。任务是最大化集合 \(\mathcal{H}\) 的大小。如果有多个解,可以输出任何一个。 曼哈顿距离:单元格 (x_1,y_1) 和 (x_2,y_2) 之间的曼哈顿距离等于 \(|x_1-x_2|+|y_1-y_2|\)。 输入数据格式:第一行包含一个整数 \(t\)(\(1≤t≤50\))——测试用例的数量。接下来的 \(t\) 行,每行包含一个整数 \(n\)(\(2≤n≤10^3\))。 输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,输出 \(n\) 个点,使得集合 \(\mathcal{H}\) 的大小最大化。每个测试用例的答案结束时不需要输出空行。 示例输入输出已给出,请参考题目描述中的样例。