401636: GYM100503 D Sequence analysis
Description
You are given a sequence of signed 64-bit integers defined as follows:
- x0 = 1,
-
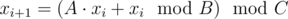 ,
,
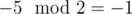 in programming, while
in programming, while 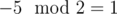 in mathematics). Use "long long" type in C++, "long" in Java and "int64" in Delphi to store xi and all other values.
in mathematics). Use "long long" type in C++, "long" in Java and "int64" in Delphi to store xi and all other values.Let's call a sequence element xp repeatable if it occurs later in the sequence — meaning that there exists such q, q > p, that xq = xp. The first repeatable element M of the sequence is such an element xm that xm is repeatable, and none of the xp where p < m are repeatable.
Given A, B and C, your task is to find the index of the second occurrence of the first repeatable element M in the sequence if the index is less or equal to 2·107. Per definition, the first element of the sequence has index 0.
InputThe only line of input contains three signed 64-bit integers: A, B and C (B > 0, C > 0).
OutputPrint a single integer — the index of the second occurence of the first repeatable member if it is less or equal to 2·107. Print - 1 if the index is more than 2·107.
ExamplesInput2 2 9Output
4Input
2305843009213693951 1 9223372036854775807Output
5Input
-2 1 5Output
4Note
In the first sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, 3, 7, 6, 3, 7. The first repeatable element is 3. The second occurence of 3 has index 4.
In the second sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, 2305843009213693951, -4611686018427387903, 6917529027641081855, 0, 0, 0. The first repeatable element is 0. The second occurence of 0 has index 5.
In the third sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, -2, 4, -3, 1, -2, 4. The first repeatable element is 1. The second occurence of 1 has index 4.