403168: GYM101059 C Gangsters
Description
You live in a graph G, with N vertices and M edges. P of these vertices have gangsters living on them. You owe each gangster some money, given by the array C (of size P). You wish to travel from s to t. If you step within distance k of any gangster who you haven't paid, you die. We define the length of a path as then number of edges it comprises. We define the distance of two nodes as the length of the shortest path connecting them. Further, we define the cost of travelling as the sum of gangster debts you pay off. Of course, you wish to minimise the cost of travelling from s to t without dying. Note that you may not die at s or t either.
InputFirst line contains four integers, N, M, P, and K. (1 ≤ N, M, K ≤ 105, 1 ≤ P ≤ 10) Second line contains P integers, the locations of the gangsters. Third line contains P integers, the array C (1 ≤ Ci ≤ 109) Each of the next M line contains two integers, xi and yi, which mean that there exists an edge between the nodes xi and yi. The last line contains two integers, s and t, the source and the target. It is guaranteed that a solution always exists.
OutputA single integer, the minimum cost of travelling from s to t.
ExampleInput5 5 1 1Output
4
100
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 5
4 5
1 5
100Note
For the given example, the graph looks like 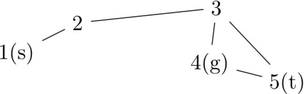 Note that the gangster is at distance 1 from the nodes 5 and 3, both of which must be visited.
Note that the gangster is at distance 1 from the nodes 5 and 3, both of which must be visited.